除了电生理和生化因素影响,力学因素也会影响脑疾病的发生发展。在综述中介绍了力学因素对脑出血(intracerebral hemorrhage, ICH),阿尔兹海默病(Alzheimer’s disease, AD),弥散性轴索损伤(diffuse axonal injury, DAI)和脑肿瘤(brain tumor)的影响。此外,综述中还介绍了体外模型用于细胞和组织的力学加载。
该综述是由郭廷旺博士主要完成,相关研究已经发表在《Current Pharmaceutical Design》。
http://www.benthamscience.com/journals/current-pharmaceutical-design/article/146755/
The underestimated role of mechanicalstimuli inbrain diseasesand the related in vitro models
Tingwang Guo, Peng Ren, Shilei Hao*, Bochu Wang*
Abstract
Background:Besides the well-documented biochemical and electrophysiological effects, the mechanical stimuli also have prominent roles in the initiation and development of brain diseases but yet have been underestimated. To explore the role of mechanical stimuli and the followed mechanical-biochemical effects in the brain diseases.
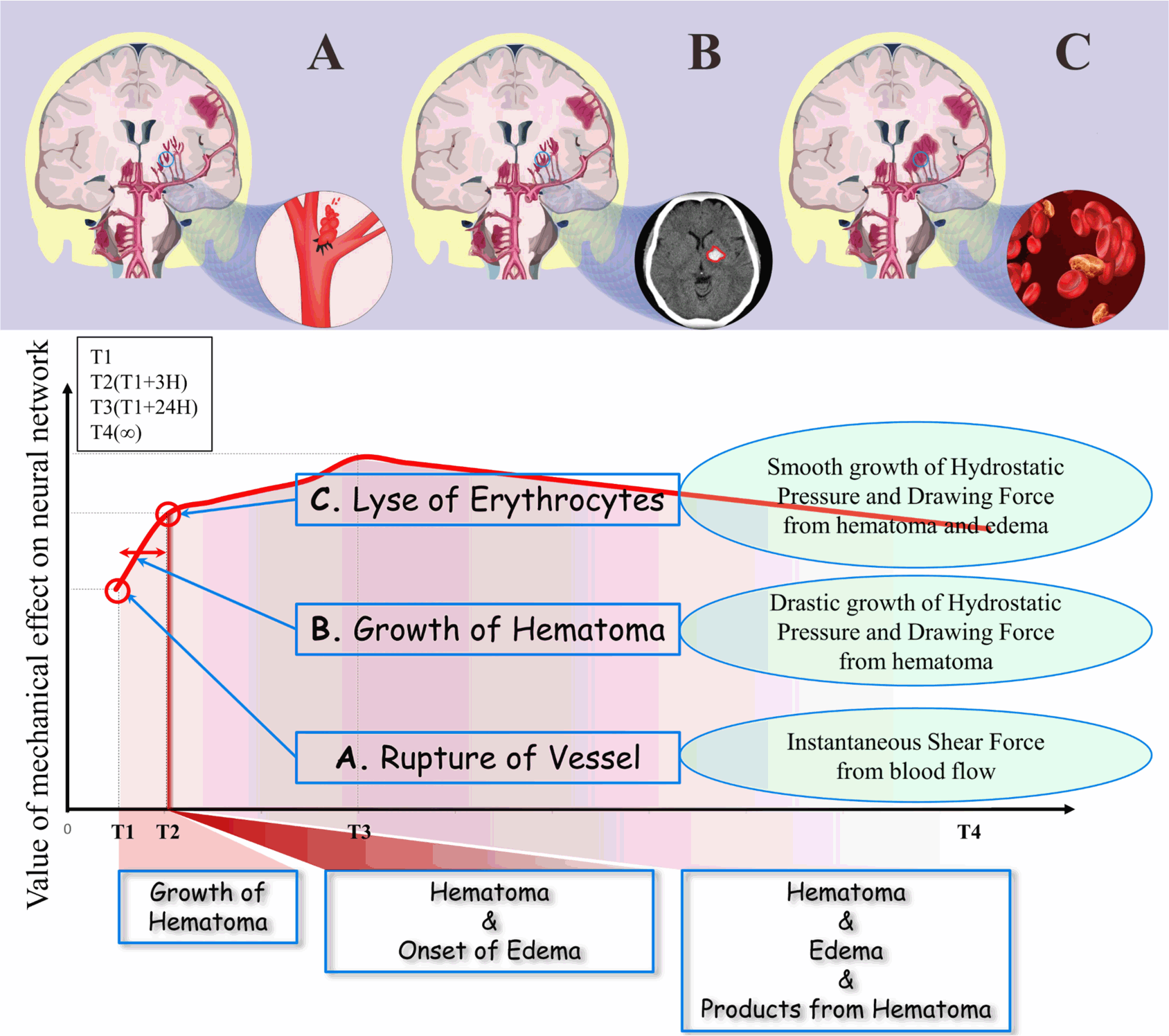
Method:In this review, we discussed the initiation and effect of mechanical stimuli and the surrounding topography in brain diseases, especially for the intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), Alzheimer’s disease (AD), diffuse axonal injury (DAI) and primary brain tumors. The induced cascades of biological pathways by mechanical stimuli prior to and during the brain diseases were summarized. Strategies aiming to reduce the mechanical stimuli related damages or poor outcomes were also discussed, despite some could only prevent rather than cure. Literatures have indicated mechanical stimuli were the connection between the exogenous mechanotransduction and the inherent biochemical cascades. Therefore, we also reviewed in vitro models in the literatures that simulated the diverse range of mechanical stimuli, which connected the neural network with the tissue engineering, biomaterials andpotential therapeutic strategies together.
Results:At the microscopic andmacroscopic levels, the hydrostatic pressure, tensile/compressive force, shear force, and even the roughness of topography from the physical surrounding exert the influence on the neural network not only by themselves but also through the interaction with other factors, e.g. biochemical or electrophysiological effects.
Conclusion:In the clinical management, taking the undervalued mechanical stimuli and the followed mechanical-biochemical effects into consideration are important and inevitable in preventing and treating brain diseases.