课题组前期已经成功从羽毛和人发中提取了角蛋白,并应用于止血和组织修复中。鉴于角蛋白良好的生物相容性和促细胞增殖特性,课题组成功构建了角蛋白/PVA纳米粒纤维,通过PVA的引入,增加了角蛋白纤维的力学特性。相关研究已发表在Materials Science and Engineering C, 72 (2017) 212–219。该课题由王驹硕士和周桃同学主要完成。
Keratose/poly (vinyl alcohol) blended nanofibers: Fabrication and biocompatibility assessment.
Ju Wang, Shilei Hao⁎, Tiantian Luo, Tao Zhou, Xin Yang, Bochu Wang⁎
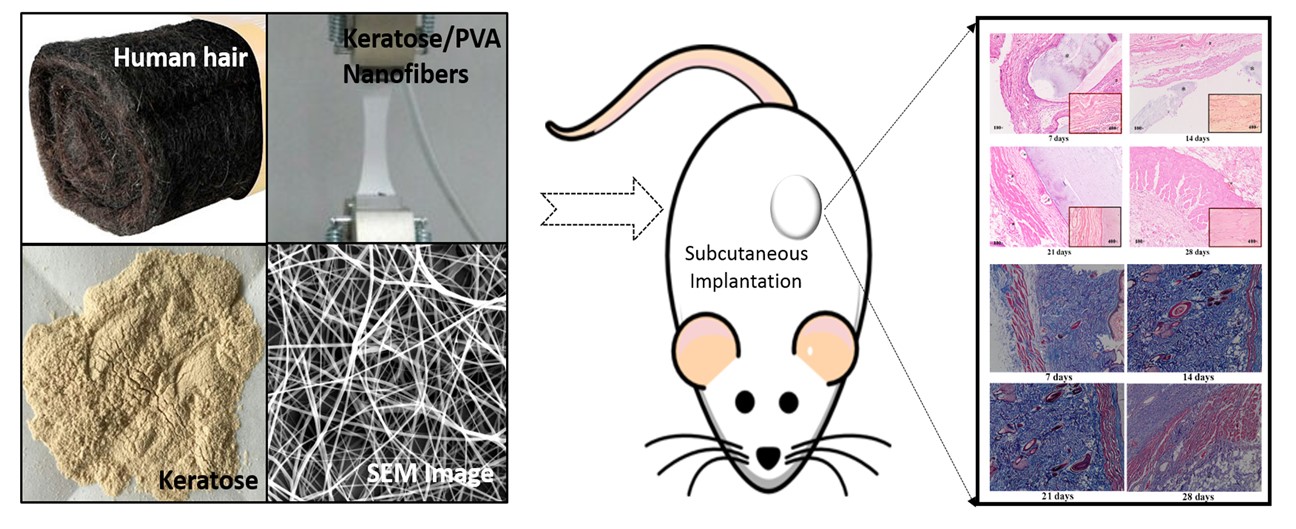
Increasing interest in using keratin-based materials for biomedical application has prompted the development of keratin/PVA nanofibers. To date, several kinds of keratins (including wool, feather, and human hair reductive keratins)/PVA blended nanofibers have been fabricated but limited to thein vitrostudies. However, few studies focused on thein vivobiocompatibility test of keratin/PVA nanofibers. Herein, the keratose (oxidative keratin)/PVA nanofiber, a novel type of keratin/PVA nanofiber, was fabricated with an electrospinning technique. The obtained nanofibers possess uniformfibrous structure, suitable hydrophilicity and mechanical properties, which could be affected by the mass ratio of keratose to PVA. Furthermore, the biocompatibility tests of keratose/PVA nanofibers have been performed by subcutaneous implantation into SD rats. H&E staining and Masson's trichrome stainingrevealed that the implants were highly compatible with body tissue, and no acute toxic effects as well as no tissue damage were observed. The implants were fully degraded within four weeks. Beyond this, the analysis of proinflammatory cytokines in rat serum indicated that the implants induced normal immune response and had no immunogenicity. These results demonstrate that keratose/PVA nanofibers have the potential for biomedical applications due to the favorable biocompatibility and biodegradability.