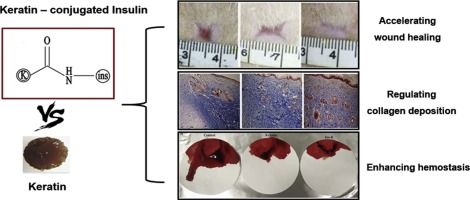
课题组前期已经对人发角蛋白的止血和组织修复功能已经研究,基于此,通过将角蛋白与胰岛素进行接枝,借助胰岛素可在组织修复过程中调控胶原排列的作用,接枝物与角蛋白相比表现出更强的组织修复效果,并其具有调控胶原排列的功能,从而具有抑制疤痕的潜力。
该课题由李文凤、高飞燕共同完成。发表在Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces。https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0927776518309007

Abstract
Accelerating and regulating collagen formation during wound healing repair is key issues for skin regeneration. Insulin can promote the healing of damaged skin by stimulating cellular migration and angiogenesis. Here, human hair keratin-conjugated insulin was synthesized to enhance full-thickness skin regeneration based on the excellent wound healing and hemostatic effects of keratin and the collagen deposition regulation ability of insulin. The insulin-conjugated keratin (Ins-K) was synthesized through the EDC/NHS reaction, which can supply a sustained release of insulin. The Ins-K hydrogel displayed similar water absorption, porosity and rheology properties to those of the keratin hydrogel. However, the Ins-K hydrogel shows a stronger hemostatic ability than the keratin hydrogel group, with a stronger wound healing effect found for the Ins-K hydrogel in the early regeneration stage (first 2 weeks) than for the keratin hydrogel treatment, resulting in smoother skin tissues at an excision section realized by regulating transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) and hydroxyproline (HYP) expression. The results demonstrate that keratin promotes hemostasis and wound healing after insulin conjugation, which highlights the potential of keratin-based materials in tissue regeneration applications.