本课题组前期发现,在体外,TUDCA 可以以 TCDCA 为底物,通过两步酶促反应转化而来:首先,TCDCA 由 7α-羟基类固醇脱氢酶(7α-HSDH)氧化为牛磺 7 酮石胆酸(T7-KLCA),然后,T7-KLCA 由 7β-羟基类固醇脱氢酶(7β-HSDH)还原为 TUDCA。基于此,我们挖掘了新的7α-HSDH(命名为St-2-1),并对其进行了功能表征,研究发现St-2-1为目前发现的唯一一个嗜酸酶。本研究扩展了7α-HSDHs的天然酶库,为应用生物催化技术大规模制备TUDCA提供了新的资源。
课题由唐士金同学完成。发表在PROTEIN SCIENCE, 2019 28(5), 910-919.
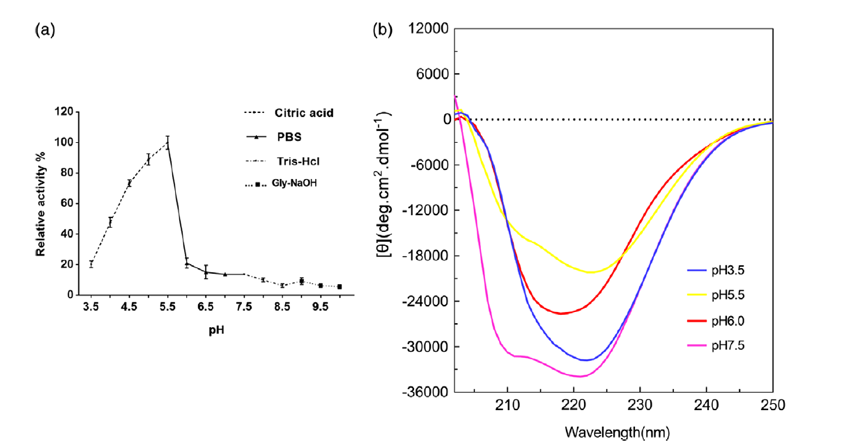
Abstract: 7α-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7α-HSDH) is an NAD(P)H-dependent oxidoreductase belonging to the short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases. In vitro, 7α-HSDH is involved in the efficient biotransformation of taurochenodeoxycholic acid (TCDCA) to tauroursodeoxycholic acid (TUDCA). In this study, a gene encoding novel 7α-HSDH (named as St-2-1) from fecal samples of black bear was cloned and heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli. The protein has subunits of 28.3 kDa and a native size of 56.6 kDa, which suggested a homodimer. We studied the relevant properties of the enzyme, including the optimum pH, optimum temperature, thermal stability, activators, and inhibitors. Interestingly, the data showed that St-2-1 differs from the 7α-HSDHs reported in the literature, as it functions under acidic conditions. The enzyme displayed its optimal activity at pH 5.5 (TCDCA). The acidophilic nature of 7α-HSDH expands its application environment and the natural enzyme bank of HSDHs, providing a promising candidate enzyme for the biosynthesis of TUDCA or other related chemical entities.